办公室:B1-309
研究方向:聚集诱导发光分子的设计合成、新颖纳米结构构筑、分子界面组装
研究领域:先进功能材料的设计及表界面分析
一、 个人简介
深圳大学化学系三级教授,深圳市杰出青年基金获得者(2011),深圳大学优秀学者(2015)。2004年获得中国科学院大学理学博士学位(导师:白春礼院士/唐本忠院士),1999.08-2001. 07 香港科技大学物理系、化学系任研究助理, 2004.09-2007.09 多伦多大学化学系 博士后(合作导师 Cynthia Goh)。
聚集诱导发光分子(aggregation-induced emission, AIE)由香港科技大学唐本忠院士研究组最先发现并命名,目前是材料科学研究领域的第二大热点课题。本课题组研究方向包括AIE分子的设计、合成、光学性质及组装结构研究;多重刺激响应AIE分子的设计和性质研究;两亲性AIE分子在表/界面上的组装行为研究;生物大分子间相互作用研究;功能高分子的光学性质和组装行为研究。
目前,已在国际著名杂志《Nano Lett》、《ACS Nano》、《Adv. Func. Mater.》、《Mater. Horizon》、《Macromolecules》、《J. Mater. Chem.C》、《J Phys. Chem. C》、《Langmuir》等发表多篇有影响力的论文。多次在中国化学会手性科学会议和AIE国际会议做邀请报告。
二、科研项目
主持深圳市杰出青年基金(2011.6)60万
主持国家自然科学青年基金项目(2013.1-2015.12)25万
主持国家自然科学基金面上项目(2016.1-2019.12) 78万
核心成员 广东省研究创新群体子课题(2016.1 –2020.12) 300(55)万
主持深圳市基础研究项目(2017.5–2019.5)30万
广东省基础研究项目(2017.1 -2020.2) 10万
副组长深圳大学交叉学科创新团队(2018,12-2022,12) 300万
三、 获奖情况
2001、2002年中科院化学所青年化学奖
2013 深圳市杰出青年基金
四、课题组成员



五、研究方向简介
一、发光纳米超螺旋纤维的构筑
通过氨基酸、胆固醇等手性取代基诱导AIE分子骨架产生螺旋构象进而形成超分子螺旋纤维。所制备的纳米/微米螺旋纤维具有圆二色性、圆偏振发光特性,是重要的发光微纳器件材料。
代表性工作 基于AIE小分子的发光纳米螺旋纤维的构筑
Small, 2016,12,6593-6601(封面论文) 共同第一作者为研究生Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2017, 1, 646(封面论文)第一作者为研究生. ACS Nano 0.1021/acsnano.9b00218 2019 in press



课题组制备的具有圆偏振发光特性的发蓝色荧光的超螺旋纤维
代表性工作 基于AIE高分子发光纳米囊泡、纳米纤维的制备(J. Mater. Chem. C. 2018,6,4807)


二、超分子组装的表/界面研究
超分子结构的形成不仅决定于分子的化学结构,而且受环境因素,如溶剂、表面界面的影响。揭示分子化学结构与外部因素对分子组装的协同作用,对于设计具有特定结构的功能材料具有重要意义。
代表性工作一(共同第一作者为研究生,J. Phys. Chem. C. 2019, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b02205 • in press)

(A) 溶液中组装的超螺旋纤维 (B、C) 液固界面上直接组装成的取向纤维


原子力显微镜揭示的界面上螺旋纤维的组装过程
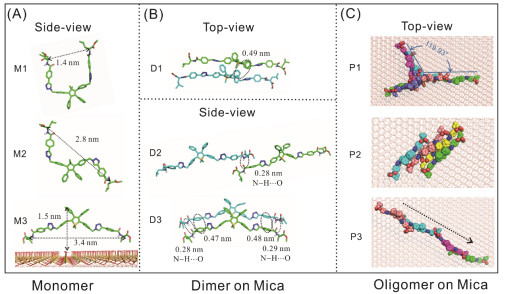
分子在溶液与界面组装的理论模拟
代表性工作二缬氨酸取代四苯乙烯分子组装的界面效应(第一作者为研究生,Langmuir. 2019, 2019, 35, 3805)
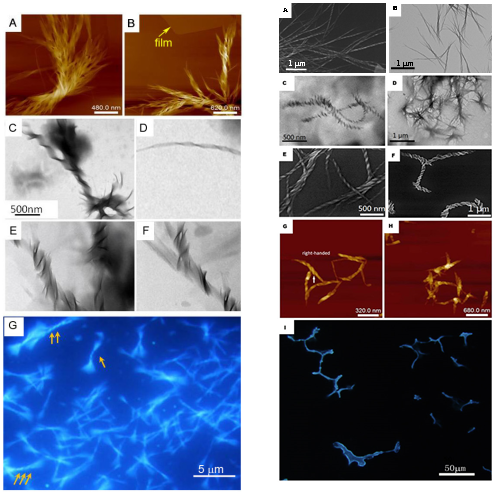
(左)缬氨酸单取代四苯乙烯分子形成的不同超螺旋带、纤维。
(右)缬氨酸双取代的四苯乙烯分子形成的不同超螺旋带、纤维。


单分子LB膜的制备
三:多重响应AIE材料的设计合成
设计基于AIE骨架的气体、pH响应、力致变色材料, 代表性研究工作发表在材料学著名杂志Adv. Funct. Mater. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.2019005162019,in press,该研究工作被高分子科学前沿介绍。

刺激响应荧光分子是一类重要的可用于光学传感器制备的功能材料。目前已经报道的刺激响应荧光分子普遍具有单一响应的特点,难以满足多元化的应用需求,而多重刺激响应荧光分子的设计具有很大挑战。最近,深圳大学李冰石教授课题组和香港科技大学唐本忠院士课题组设计出了一种具有多重刺激响应功能的聚集诱导发光分子(aggregation induced emission,AIE)。该分子除了对pH和胺蒸气响应之外,还具有三色快速可逆力致变色的功能。目前报道的力致变色荧光小分子只有两色变化,多色力致变色并不多见,而能够进行快速、可逆、高反差多色变化的分子则更少。
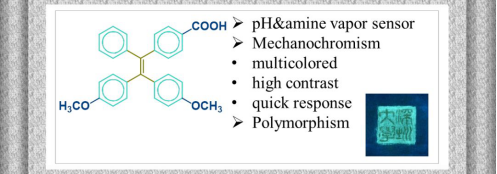
图1. 分子1的结构和多重响应的特点。
“五味俱全”的AIE小分子
该分子的制备基于四苯乙烯骨架,辅助修饰以一个羧基和两个甲氧基,可以说是一点点“原料”和“辅料”一锅就烩出的“菜品”却具有“五味俱全”的神奇功效。主要体现在:
1. AIE性质和pH响应功能。AIE性质是四苯乙烯骨架与生俱来的,在这基础上,羧基的引入带来了pH响应功能(图2);

图2. 分子1的(a, b)AIE性质和(c-f)pH响应性质。
2. 胺蒸气传感器。基于分子1制备的试纸传感器,在17种胺类蒸气中,对二丙胺蒸气具有特异性响应。表现出传感器的荧光颜色具有肉眼可辨的明显变化(图3);
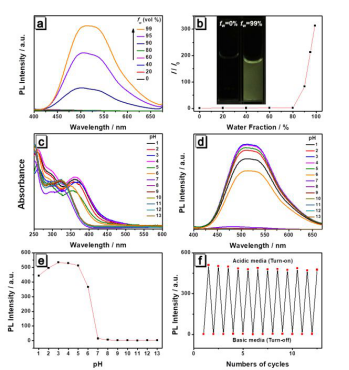
图3 分子对不同类型胺的荧光响应和对应荧光光谱
力致/热致/溶剂变色性质。分子1的粉末在经过研磨(1p-g),溶剂饱和蒸汽熏(1p-f)和140摄氏度加热(1p-h)后,具有不同的荧光颜色,分别发黄色,蓝色和青色荧光(图4a和4b)。1p-h的荧光量子产率高达82.3%,差不多是另两种状态的十倍。且这三种状态的相互转变都能在几分钟之内完成。从粉末XRD数据分析,1p-g的结晶度最低,而1p-f和1p-h都具有高结晶度,但二者具有不同的分子堆积模式(图4c)。利用分子1的这种多重力致变色性质,我们为读者制备了具有中国传统文化特色的“深圳大学”印章图案(图4d)。

图4. 分子1的三色力致变色性质及应用原型。
课题组活动剪影





课题组发表论文
1. Huang, G. X.; Jiang, Y. Q.; Yang, S. F.; Li, B. S.* and Tang, B. Z.* Multistimuli Response and Polymorphism of a Novel Tetraphenylethylene Derivative,Adv. Funct. Mater.DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201900516 2019,in press
2. Zhang, J., Liu, Q. M., Wu, W. J.;Peng, J. H., Zhang, H. K., Song, F. Y., He, B. Z., Wang, X. Y.§, Herman H.-Y. Sung., Chen, M., Li, B. S.*, Liu, S. H,Lam, J. W. J.,Tang, B. Z.* Real-Time Monitoring of Hierarchical Self-Assembly and Induction of CircularlyPolarized Luminescence from Achiral Luminogen ACS Nano 0.1021/acsnano.9b00218 2019 in press
3. Surface Effect on The Self-Assembly of Nanofibers Revealed by in Situ AFM Imaging and Molecular Simulation Chen, Y. T.; Xue, S.; Xia, Q.; Li, H. K.; Liu, Q. M.; Li, B. S.* and Tang, B. Z.*J. Phys. Chem. CDOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b02205 • 2019 in press
4. Li, B. S.*; Huang, X. J.; Li, H. K.*; Xia, W. J.; Xue, S.; Xia, Q.; Tang, B. Z.*; Solvent and Surface/Interface Effect on the Hierarchical Assemblies of Chiral Aggregation-Induced Emitting Molecules, Langmuir 2019, 35, 3805−3813
5. Li, H. K.; Li, B. S.*; Tang, B. Z.*,Molecular design, Circularly Polarized Luminescence and Helical Self-Assembly of Chiral Aggregation Induced Emission Molecules,Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 674 – 688
6. Huang, G.; Wen, R.; Wang, Z.; Li, B. S.; Tang B. Z.* Novel chiral aggregation induced emission molecules: self-assembly, circularly polarized luminescence and copper(II) ion detection Mater. Chem. Front. 2018, 2, 1884
7. Liu, Q.; Xia, Q.; Wang, S.;Li, B. S.*; Tang B. Z.* In situ visualizable self‐assembly, aggregation induced emission and circularly polarized luminescence of tetraphenylethene and alanine based chiral polytriazole J. Mater. Chem. C.2018,6,4807
8. Xue, S.; Meng, L.; Wen, R.; Shi, L.; Lam, J. W.; Tang, Z.; Li, B. S.*;Tang, B.Z. *Unexpected aggregation induecd circular dichoism, circular polarized luminescence and helical assembly from achiral hexaphenylsilole(HPS), RSC Advances, 2017, 7, 24841
9. Li, H.;Li, B. S.*; Tang, B. Z. * Helicity, assembly, and circularly polarized luminescence of chiralAIEgensProc. of SPIE,invited keynote paper,2016,Vol. 9940 99400A-1-99400A-8.
10. Li, H., Xue, S.;H. Su B. Shen, Z. Cheng. J. W. Y. Lam, Kam Sing Wong,H. Wu, Li,B. S.*, Tang B. Z.*, Nanofibers: Click Synthesis, Aggregation-Induced Emission and Chirality, Circularly Polarized Luminescence, and Helical Self-Assembly of a Leucine-Containing Silole (封面论文) Small, 2016,12,6593-6601
11. Li, B. S.*; Wen R.; Xue S.; Shi L.; Tang, Z. Y.; Wang, Z, M.b; Tang, B. Z.* Fabrication of circular polarized luminescent helical fibers from chiral phennanthro[9,10]imidazole derivatives,Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2017, 1, 646
12. Li,H.; Cheng,J.; Deng,H.; Zhao,E.; Shen,B.; J. W. Y. Lam,; Wong, C.; Wu,K. S.; Li, B. S.*; Tang, B. Z.*, Synthesis, optical properties, and helical self-assembly of a bivalinecontaining tetraphenyletheneSci. Rep.2016, DOI: 10.1038/srep19277
13. Li,H.; Cheng, J.; Deng,H.; Zhao, E.; Shen, B.; J. W. Y. Lam,; Wong, C.; Wu, K. S.; Li, B. S.*; Tang, B. Z.*, Aggregation-induced chirality, circularly polarized luminescence, and helical self-assembly of aleucine-containing AIE luminogen J. Mater. Chem. C.2015, 3,2399 – 2404.
14. Li, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Wong, K. S.; Wu, H.; Li, B. S.*; Tang, B. Z.*L-Valine methyl ester-containing tetraphenylethene: aggregation-induced light emission and circular dichroism, circularly polarised luminescence, and helical self-assembly Mater. Hori. 2014,1(5),518-521
15. Ng,J. C. Y.; Li, H.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Fan, X.; Li, B. S.* and Tang, B. Z.* Valine containing silole, synthesis, aggregation induced chirality, luminescence enhancement, chiral polarized luminescence and self-assembled structures J. Mater. Chem. C, 2014, 2 (23), 4615 - 4621
16. Li, B. S.*; Lam, J. W. Y.; Yu, Z. and Tang, B. Z.Tunable Helical Assemblies of l-Alanine Methyl Ester-Containing Polyphenylacetylene Langmuir, 2012, 28 (13), pp 5770–5774
17.Li, B. S.*; Wei, B.; M. C. Goh Direct visalization of the formation of RecA/dsDNA complexes at the single-molecule level Micron, 2012, 43,1073-1075
18. Li, B. S.; Goh, C.*, Direct Evidence of the Role of ATPγS in the Binding of Single-Stranded Binding Protein (Escherichia coli) and RecA to Single-Stranded DNA Langmuir, 2010,26, 14755-14758
19.Li,B. S.; Goh, C.* Direct visualization of the formation and structure of RecA/dsDNA complexes Micron, 2010,41,227-231.
20. Cheuk, K. K. L.; Li, B. S.; Lam,J. W. Y.; etc. Synthesis, Chain Helicity, Assembling Structure, and Biological Compatibility of Poly(phenylacetylene)s Containing L-Alanine Moieties Macromolecules, 2008, 41, 5997–6005
21. Cheuk,K. K. L.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Li, B. S.; Xie, Y. and Tang, B. Z. Decorating Conjugated Polymer Chains with Naturally Occurring Molecules: Synthesis, Solvatochromism, Chain Helicity, and Biological Activity of Sugar-Containing Poly(phenylacetylene)s Macromolecules, 2007, 40(8), 2633-2642.
22. Goh, C.*; Li, B. S. Reply to Comment on “Direct and Real-Time Visualization of the Disassembly of a Single RecA-DNA-ATPçS Complex Using AFM Imaging in Fluid”, Nano Lett., 2007, 7(4): 1110-1111
23.Li, B. S.; Sattin, B.; Goh, C. Direct and real-time visualization of the disassembly of a single RecA-DNA-ATP gamma S complex using AFM imaging in fluid, Nano Lett., 2006, 6 (7): 1474-1478
24. Li, C. J.; Guo, Y. G.; Li, B. S.; Wang, C. R.; Wan, L. J.; Bai, C. L. "Template Synthesis of Sc@C82 Nanowires and Nanotubes at Room Temperature" Adv. Mater. 2005, 17(1), 71-73
25.Li, B. S.; Kang, S. Z. etc. Self-assembling of polyacetylene bearing amino acid attachment on mica, in solution and on water surface Langmuir, 2004, 20, 7598-7603
26. Li, B. S.; Chen, J.; Zhu, C. etc. Formation of vesicular fibers and porous film from chiral oligomers, Langmuir 2004, 24, 2515-2518. 14.B.S. Li, K.K.L. etc. Self-assemblying of an Amphiphilic Polyacetylene Carrying L-Leucine Pendants Macromolecules, 2003, 36, 5447-5440.
27.Li, B. S.; Cheuk, K. K. L. etc. Synthesis and hierarchical structures of amphiphilic polyphenylacetylenes carrying L-valine pendants Macromolecules, 2003, 36, 77-85.
28.Li, B. S.; Li, G.; Wang, C.; M. etc. Structure-governed growth phenomenon of a Trichosanthin crystal, Langmuir, 2002, 18, 6723-6726.
29.Li, B. S.; Cheuk, K.K.L. etc. Tuning the chain helicity and Organizational Morphology of an an L-valine-containing polyphenylacetylene by pH Change, Nano Lett., 2001, 6, 323.
论著章节
1.Li, B. S.; Cheuk, K.K.L.; Chen, J.; Xiao, X.; Bai, C.; Tang, B. Z. “Vesicular and Tubular Nanoassemblies of an Helical Amphiphilic Polyacetylene” In Nano Science and Technology–Novel Structures and Phenomena; Tang, Z. K., Sheng, P., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: London, 2003; Chapter 9, pp 98–104.
2.Li, B. S.; Cheuk, K.K.L.; Chen, J.; Xiao, X.; Bai, C.; Tang, B. Z. “Vesicular and Tubular Nanoassemblies of an Helical Amphiphilic Polyacetylene” in Nano Science and Technology–Novel Structures and Phenomena, Chapter 9
Cheuk, K.K.L.;Li, B. S.; Tang, B. Z.“Polyacetylene Nanostructures” In Encyclopedia of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology; Nalwa, H. S., Ed.; American Scientific Publishers: CA, 2004; Vol. 8, pp 703–713 (invited review).
3. Cheuk,K. K. L.; Li, B. S.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Chen, J.; Bai, C.; Tang, B. Z. “Amphiphilic Conjugated Polymers with Tunable Chain Helicity and Organizational Morphology” In Advanced Nanomaterials and Nanodevices; Gao, H., Fuchs, H., Chen, D., Eds.; Institute of Physics Publishing Ltd: Philadelphia, PA, 2003; pp 87–107 (invited paper).
4. Tang, B. Z.; Cheuk, K. K. L.; Salhi, F.; Li, B. S.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Cha,J. A. K.; Xiao, X. D. In Synthetic Macromolecules with Higher Structure order, Khan, I.M., Ed.; American Chemistry Society: ACS Symposium Series 812, Washington, DC, 2001 chapter 10, pp 133–148.
课题组欢迎本科生、研究生、博士后申请
六、联系方式
e-mail: phbingsl@szu.edu.cn
Tel: 26558094 (o)
七、对学生基本要求
勤于思考、勇于探索、大胆求证、锲而不舍
